Title: Synergetic Effect of Ru and NiO in Electrocatalytic Decomposition of Li2CO3 for Enhancing the Performance of Li-CO2/O2 Battery
Authors: Pengfang Zhang, Jun-Yu Zhang, Tian Sheng, Yan-Qiu Lu, Zu-Wei Yin, Yu-Yang Li, Xinxing Peng, Yao Zhou, Jun-Tao Li, Yijin Wu, Jin-Xia Lin, Bin-Bin Xu, Xi-Ming Qu, Ling Huang, Shi-Gang Sun
Abstract:
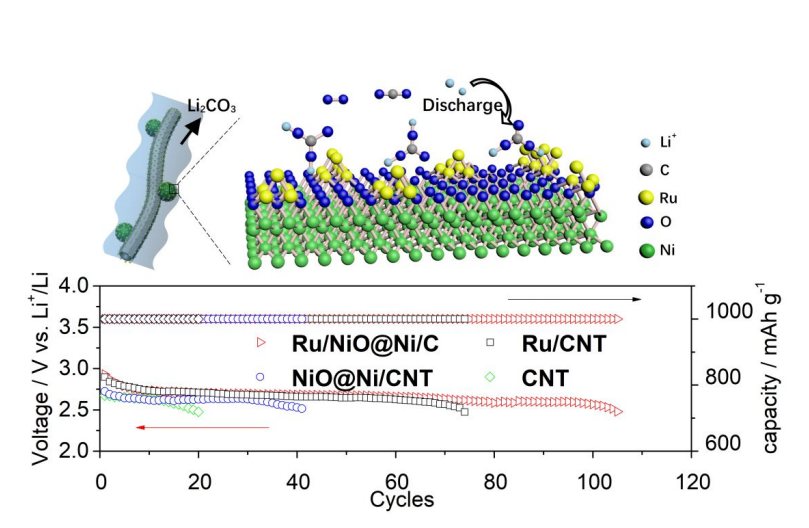
Li2CO3 is the cathodic discharge product of Li-CO2/O2 battery and is difficult to electrochemically decompose. The ac-cumulation of Li2CO3 leads to the battery degradation and results in short life span. Herein, a carbon nanotube sup-ported Ru/NiO@Ni catalyst (Ru/NiO@Ni/CNT) is synthesized with Ru nanoparticles ( 2.5 nm) anchored on the sur-face of core-shell structure NiO@Ni nanoparticles (17 nm). We found a strong interfacial interactions between Ru nanoparticles and NiO. XRD and XPS analysis revealed that the presence of Ru could protect the Ni species from being deep oxidized while the NiO species could modify the local electronic structure of Ru inducing higher oxidation state. When such Ru/NiO@Ni/CNT catalyst is used as cathode in Li-CO2/O2 (V:V=4:1) batteries, an along cycling life of 105 cycles at a cut-off capacity 1000 mAh g-1 with overpotential as low as 1.01 V was achieved, which is significantly better than 75 and 44 cycles with Ru/CNT and NiO@Ni/CNT catalysts, respectively, and confirms the strong synergetic effect between the Ru and NiO species in electrocatalytic decomposition of Li2CO3. Density functional theory (DFT) calcula-tions of electrochemical decomposition of Li2CO3 with the assistance of RuO2 indicates that the formation O2 is the rate determining step. And the formation and decomposition process of Li2CO3 was illuminated at a molecule level by in-situ FTIRs spectroscopy with Ru/NiO@Ni/CNT catalysts.
Full-Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acscatal.9b04138