Title: Conductive polyaniline doped with phytic acid as a binder and conductive additive for a commercial silicon anode with enhanced lithium storage properties
Authors: Chengkun Zhang, Qiulin Chen, Xin Ai, Xiaogang Li, Qingshui Xie, Yong Cheng, Hufan Kong, Wanjie Xu, Laisen Wang, Ming-Sheng Wang, Hui Yang and Dong-Liang Peng
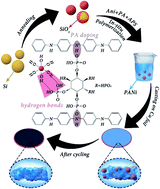
Abstract: Silicon (Si) has been regarded as a promising alternative anode to the commercial graphite for high performance lithium ion batteries (LIBs) because of its ultrahigh theoretical capacity. However, the dramatic volume expansion during cycling and poor electronic conductivity of Si restrict its electrochemical performance. Herein, a three-dimensional (3D) conductive polyaniline (PANi) is synthesized through in situ polymerization and used as both a binder and a conductive additive for commercial Si nanoparticles (SiNPs) to improve their electrochemical performance. The designed Si@SiOx/PANi-100 integrated anode shows high specific capacity and excellent cycling stability and rate capability. A high reversible capacity of 1137 mA h g−1 is obtained after 500 cycles at a current density of 1 A g−1. The influences of PANi on the electrode structural stability and ionic and electronic conductivities of Si-based anodes are investigated in detailed by in situ TEM, ex situ SEM, XPS characterization and chemo-mechanical simulation. The results could deepen the understanding of the intrinsic electrochemical behavior of the Si anode during cycling, and the designed 3D conductive PANi could also be used in other advanced electrode materials for high-performance LIBs.
Full-Link: https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/2020/ta/d0ta04389c#!divAbstract