Title: Diminishing Space-Charge Layer Effect of Zinc Anodes by an Anion-Immobilized Electrolyte Membrane
Authors: Yang Yang*, Haiming Hua, Zeheng Lv, Weiwei Meng, Minghao Zhang, Hang Li, Pengxiang Lin, Jin Yang, Guanhong Chen, Yuanhong Kang, Zhipeng Wen, Jinbao Zhao*, and Cheng Chao Li*
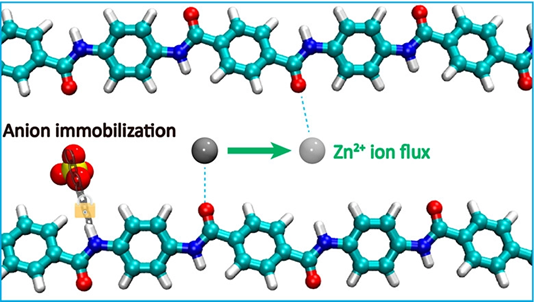
Abstract: The Zn dendrite issue, which is closely related to the creation of the space-charge region upon local anion depletion during cycling, has plagued the practical applications of aqueous Zn metal batteries (ZMBs). Herein, we propose a Kevlar-derived hydrogel (KevlarH) electrolyte with immobilized anions to diminish the space-charge layer effect. SO42– anions are strongly tethered to amide groups of polymer chains, which mitigates the concentration polarization of interfacial Zn2+ ions by preventing the anion depletion. Furthermore, the relatively weak interaction between Zn2+ cations and carbonyl groups can redistribute Zn2+-ion flux without sacrificing the ion diffusion rate. The synergistic “zincophilic” and “anionphilic” building blocks enable dendrite-free Zn deposition behavior and suppressed side reactions, thereby extending the lifespan of a Zn metal anode up to 3500 h with an ultrahigh Coulombic efficiency of 99.87%. Importantly, the KevlarH electrolyte can be directly used to assemble high-voltage bipolar ZMBs and break the 2 V barrier in aqueous ZMBs.
Full-Link: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acsenergylett.3c00385