Title: Direct conversion of methane with O2 at room temperature over edge-rich MoS2
Authors: Jun Mao, Huan Liu, Xiaoju Cui, Yunlong Zhang, Xiangyu Meng, Yanping Zheng, Mingshu Chen, Yang Pan, Zhenchao Zhao, Guangjin Hou, Jingting Hu, Yanan Li, Guilan Xu, Rui Huang, Liang Yu* & Dehui Deng*
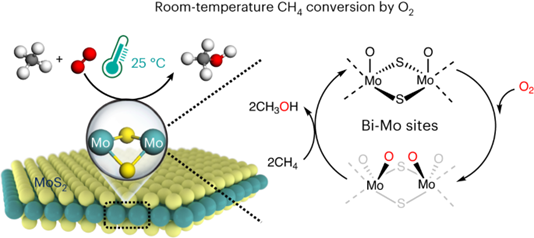
Abstract: Conversion of methane to value-added chemicals at low temperature by directly using inexpensive O2 as oxidant offers an ideal route for methane utilization but remains a great challenge due to the chemical inertness of methane and the low activity of O2. Methane monooxygenase is the only known natural catalyst that can convert methane with O2 at room temperature. Here we report the realization of an artificial process for the direct methane conversion to C1 oxygenates with O2 on an edge-rich MoS2 catalyst at 25 °C, which delivers a remarkable methane conversion of 4.2% with >99% selectivity for C1 oxygenates. In situ spectroscopic and microscopic characterizations and theoretical calculations reveal that the binuclear molybdenum sites of sulfur vacancies at the MoS2 edge can directly dissociate O2 to form O=Mo=O* active species, which can activate the C–H bond and enable methane conversion at room temperature.
Full-Link: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41929-023-01030-2